I wanted to load an Excel XML file (a.k.a. Microsoft Office Excel 2002 and Excel 2003 XML Format — SpreadsheetML) in another Excel file using Power Query M formula language. It turns out that it's trickier than I expected so I decided to blog my solution.
Many SAP related tools export this Microsoft 2003 XML format. You can save an excel file in that format by selecting the "XML Spreadsheet 2003 (*.xml)" option in the save as dialog:
Notice the "<?mso-application progid="Excel.Sheet"?>" line which gives out the type of this xml file.
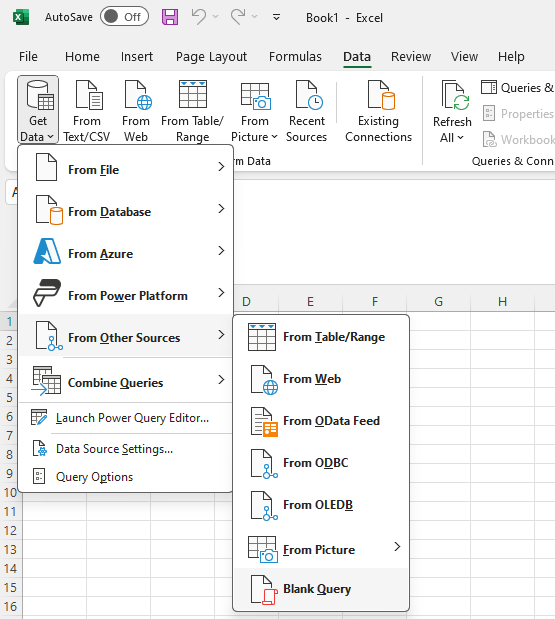
Once you have this file, let's assume you place it in C:\tmp\ExcelXmlExport.xml and you need to load it in an excel file. Open up Excel and navigate to the Data tab and then select Get Data -> From Other Sources -> Blank Query.
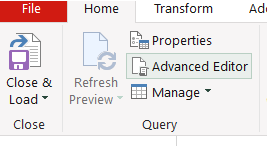
From the ribbon select the advance editor:
In the editor paste the following M script:
This will load the Excel XML file and you should have all data loaded as strings:
From there on, you can Close & Load and start building your dashboard using the data you just loaded from an external file.


No comments:
Post a Comment